Hi there! My name is Rui-Chen Zheng (郑瑞晨).
I am currently a Ph.D. candidate at National Engineering Research Center for Speech and Language Information Processing of University of Science and Technology of China, supervised by Prof. Zhen-Hua Ling.
I also closely collaborate with Dr. Yang Ai.
My main research interests include speech coding, articulatory-acoustic relationship in speech synthesis, and deep learning for speech synthesis.
My CV can be downloaded here.中文版简历.
🔥 News
- 2026.1: 🎉🎉 I am thrilled to announce that three papers have been accepted to ICASSP 2026! These include one first-author paper, one co-first-author paper, and one co-authored work. Heartfelt thanks to all my incredible co-authors for their collaboration and support!
- 2025.11: 🎉🎉 My first-authored paper, “Say More with Less: Variable‑Frame‑Rate Speech Tokenization via Adaptive Clustering and Implicit Duration Coding”, has been accepted as an oral presentation at AAAI 2026! We have open-sourced the code and model weights.
- 2025.10: 🎉🎉 I am thrilled to announce that I have received the 2025 National Graduate Scholarship! This achievement would not have been possible without the guidance and support of my supervisor, Prof. Ling, my collaborator, Dr. Ai, and my fellow lab mates. I am proud to share this honor with them. The official announcement can be found here.
- 2025.09: 🎉🎉 I am thrilled to announce that I have started an 8-month visiting position at the Centre for Speech Technology Research (CSTR) at the University of Edinburgh. I am hosted by Dr. Korin Richmond and funded by the Speech generation for Indigenous language education (SGILE) project. I’m incredibly grateful to Korin for this wonderful opportunity and look forward to the exciting research ahead.
📖 Educations
- 2021.09 - 2026.06 (Expected), Ph.D. Candidate in Information and Comunication Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China
- Supervised by Prof. Zhen-Hua Ling.
- GPA: 3.9/4.3 (Top 3%).
- 2017.09 - 2021.06, Bachelor’s Degree of Electronic Information Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China
- Thesis: Method and Practice on Text-to-speech Without Text.
- GPA: 3.89/4.3, 90.46/100 (Top 5%).
- Minor in Business Administration.
💼 Experiences
- 2025.09 - 2026.04 (Expected), Visiting Student in Centre for Speech Technology Research (CSTR), University of Edinburgh
- Hosted by Dr. Korin Richmond.
- Funded by the Speech generation for Indigenous language education (SGILE) project.
- 2025.03 - 2025.08, Research Intern, Tongyi Speech Group, Alibaba Inc.
- Advised by Dr. Qian Chen, Mr. Chong Deng, and Mr. Qinglin Zhang.
📝 Publications
🎈 Speech Coding
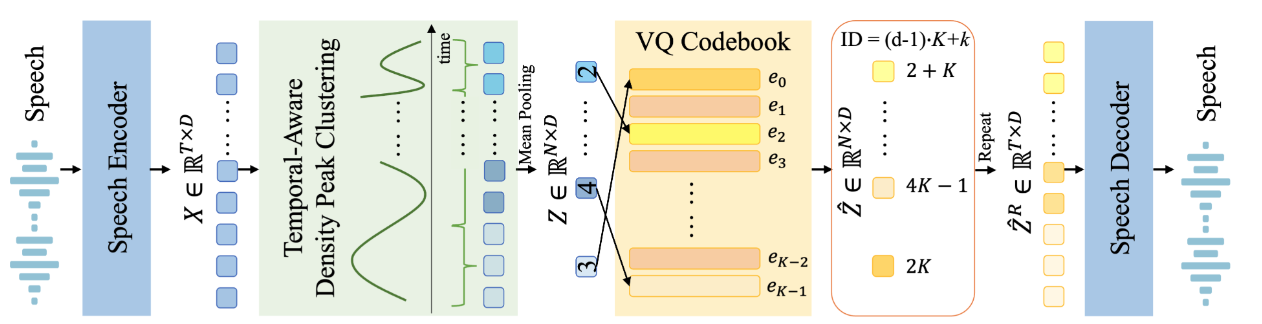
Rui-Chen Zheng, Wenrui Liu, Hui-Peng Du, Qinglin Zhang, Chong Deng, Qian Chen, Wen Wang, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
- Existing speech tokenizers typically assign a fixed number of tokens per second, regardless of the varying information density or temporal fluctuations in the speech signal. This uniform token allocation mismatches the intrinsic structure of speech, where information is distributed unevenly over time. To address this, we propose VARSTok, a VAriable-frame-Rate Speech Tokenizer that adapts token allocation based on local feature similarity. VARSTok introduces two key innovations: (1) a temporal-aware density peak clustering algorithm that adaptively segments speech into variable-length units, and (2) a novel implicit duration coding scheme that embeds both content and temporal span into a single token index, eliminating the need for auxiliary duration predictors. Extensive experiments show that VARSTok significantly outperforms strong fixed-rate baselines. Notably, it achieves superior reconstruction naturalness while using up to 23% fewer tokens than a 40 Hz fixed-frame-rate baseline. VARSTok further yields lower word error rates and improved naturalness in zero-shot text-to-speech synthesis. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to demonstrate that a fully dynamic, variable-frame-rate acoustic speech tokenizer can be seamlessly integrated into downstream speech language models.
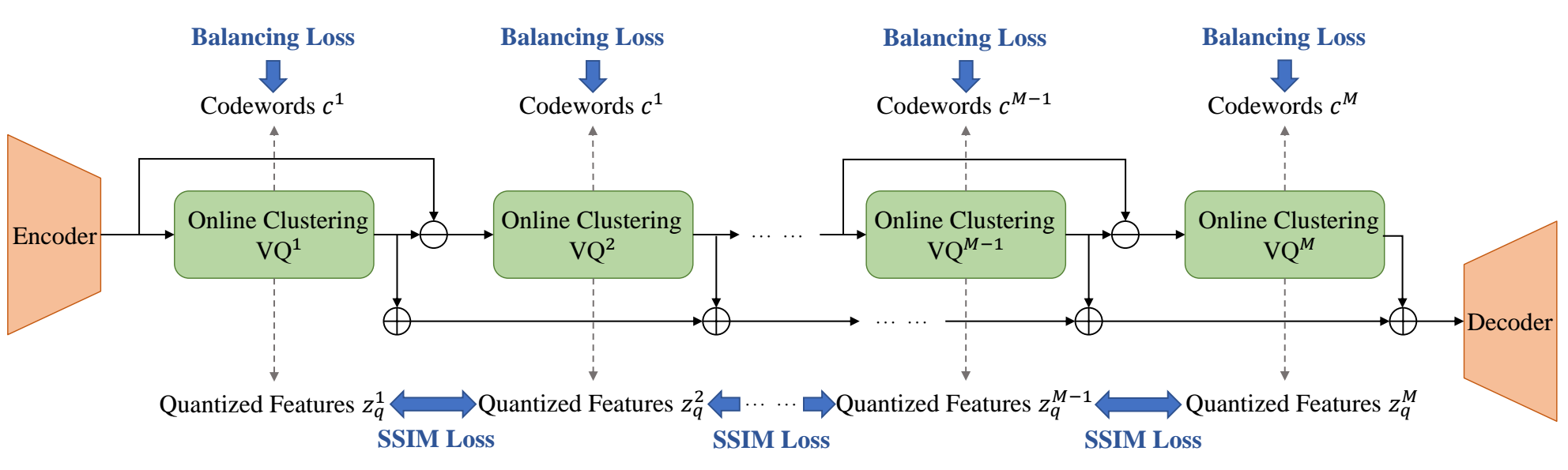
Rui-Chen Zheng, Hui-Peng Du, Xiao-Hang Jiang, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
- Current neural audio codecs typically use residual vector quantization (RVQ) to discretize speech signals. However, they often experience codebook collapse, which reduces the effective codebook size and leads to suboptimal performance. To address this problem, we introduce ERVQ, Enhanced Residual Vector Quantization, a novel enhancement strategy for the RVQ framework in neural audio codecs. ERVQ mitigates codebook collapse and boosts codec performance through both intra- and inter-codebook optimization. Intra-codebook optimization incorporates an online clustering strategy and a code balancing loss to ensure balanced and efficient codebook utilization. Inter-codebook optimization improves the diversity of quantized features by minimizing the similarity between successive quantizations. Our experiments show that ERVQ significantly enhances audio codec performance across different models, sampling rates, and bitrates, achieving superior quality and generalization capabilities. Further experiments indicate that audio codecs improved by the ERVQ strategy can improve unified speech-and-text large language models (LLMs).
- Accepted by ICASSP 2026 Enhancing Noise Robustness for Neural Speech Codecs through Resource-Efficient Progressive Quantization Perturbation Simulation, Rui-Chen Zheng, Yang Ai, Hui-Peng Du, Li-Rong Dai.
- Accepted by ICASSP 2026 CodeSep: Low-Bitrate Codec-Driven Speech Separation with Base-Token Disentanglement and Auxiliary-Token Serial Prediction, Hui-Peng Du, Yang Ai, Xiao-Hang Jiang, Rui-Chen Zheng, Zhen-Hua Ling.
-
IEEE Signal Processing Letters Is GAN Necessary for Mel-Spectrogram-based Neural Vocoder?, Hui-Peng Du, Yang Ai, Rui-Chen Zheng, Ye-Xin Lu, Zhen-Hua Ling.
-
INTERSPEECH 2025 Vision-Integrated High-Quality Neural Speech Coding, Yao Guo, Yang Ai, Rui-Chen Zheng, Hui-Peng Du, Xiao-Hang Jiang, Zhen-Hua Ling.
-
IEEE Signal Processing Letters A Streamable Neural Audio Codec With Residual Scalar-Vector Quantization for Real-Time Communication, Xiao-Hang Jiang, Yang Ai, Rui-Chen Zheng, Zhen-Hua Ling.
-
ISCSLP 2024 APCodec+: A Spectrum-Coding-Based High-Fidelity and High-Compression-Rate Neural Audio Codec with Staged Training Paradigm, Hui-Peng Du, Yang Ai, Rui-Chen Zheng, Zhen-Hua Ling.
-
SLT 2024 MDCTCodec: A Lightweight MDCT-based Neural Audio Codec towards High Sampling Rate and Low Bitrate Scenarios, Xiao-Hang Jiang, Yang Ai, Rui-Chen Zheng, Hui-Peng Du, Zhen-Hua Ling.
-
SLT 2024 Stage-Wise and Prior-Aware Neural Speech Phase Prediction, Fei Liu, Yang Ai, Hui-Peng Du, Ye-Xin Lu, Rui-Chen Zheng, Zhen-Hua Ling
-
INTERSPEECH 2024 A Low-Bitrate Neural Audio Codec Framework with Bandwidth Reduction and Recovery for High-Sampling-Rate Waveforms, Yang Ai, Ye-Xin Lu, Xiao-Hang Jiang, Zheng-Yan Sheng, Rui-Chen Zheng, Zhen-Hua Ling.
🎈 Articulation-Acoustic Relationship
🔑 Articulation-to-Speech Synthesis
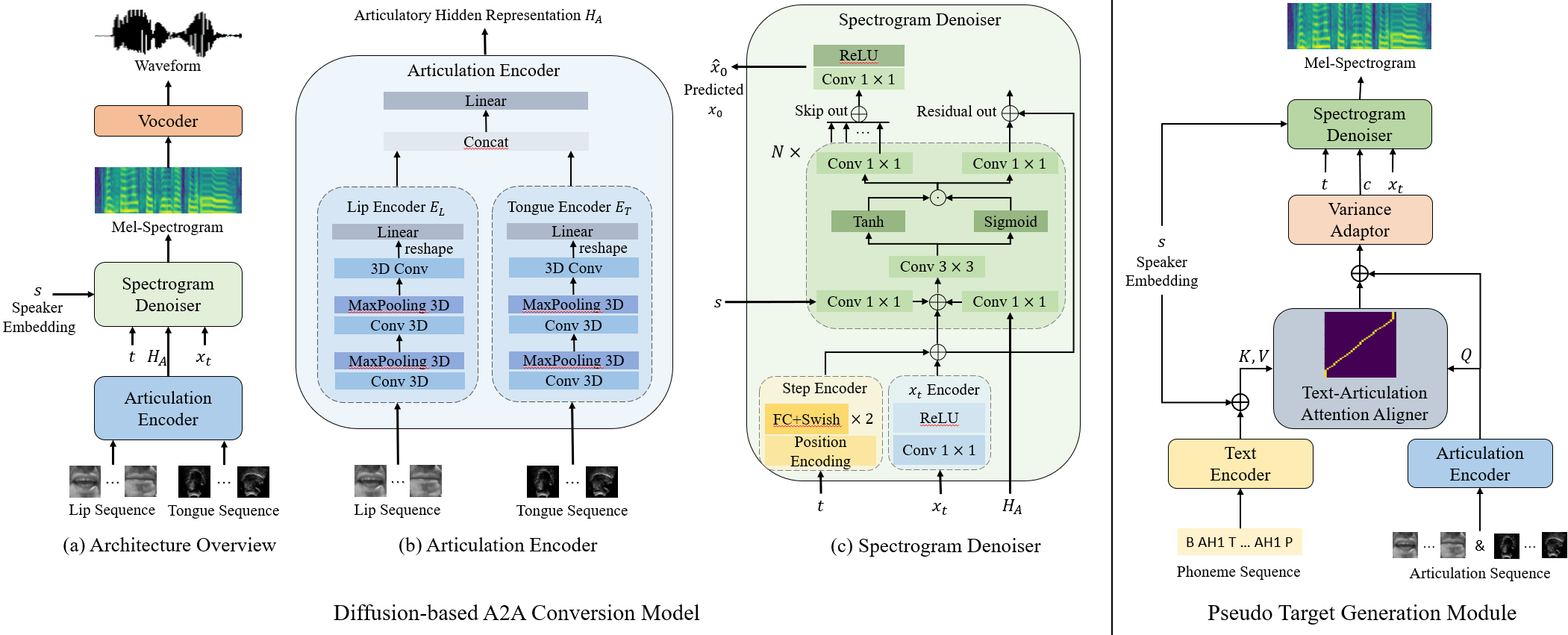
Rui-Chen Zheng, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
- This paper studies the task of speech reconstruction from ultrasound tongue images and optical lip videos, with a particular focus on a silent speaking mode, where people only activate their intra-oral and extra-oral articulators without producing real speech. We introduce a novel pseudo target generation strategy, integrating the text modality to align with articulatory movements, thereby guiding the generation of pseudo acoustic features for supervised training on speech reconstruction from silent articulation. Furthermore, we propose to employ a diffusion model as the fundamental architecture for the A2A conversion task and train the model with the pseudo acoustic features generated by the proposed pseudo target generation strategy using a combined training approach. Experiments show that our proposed method significantly improves the intelligibility and naturalness of the reconstructed speech in the silent speaking mode compared to all baseline methods.
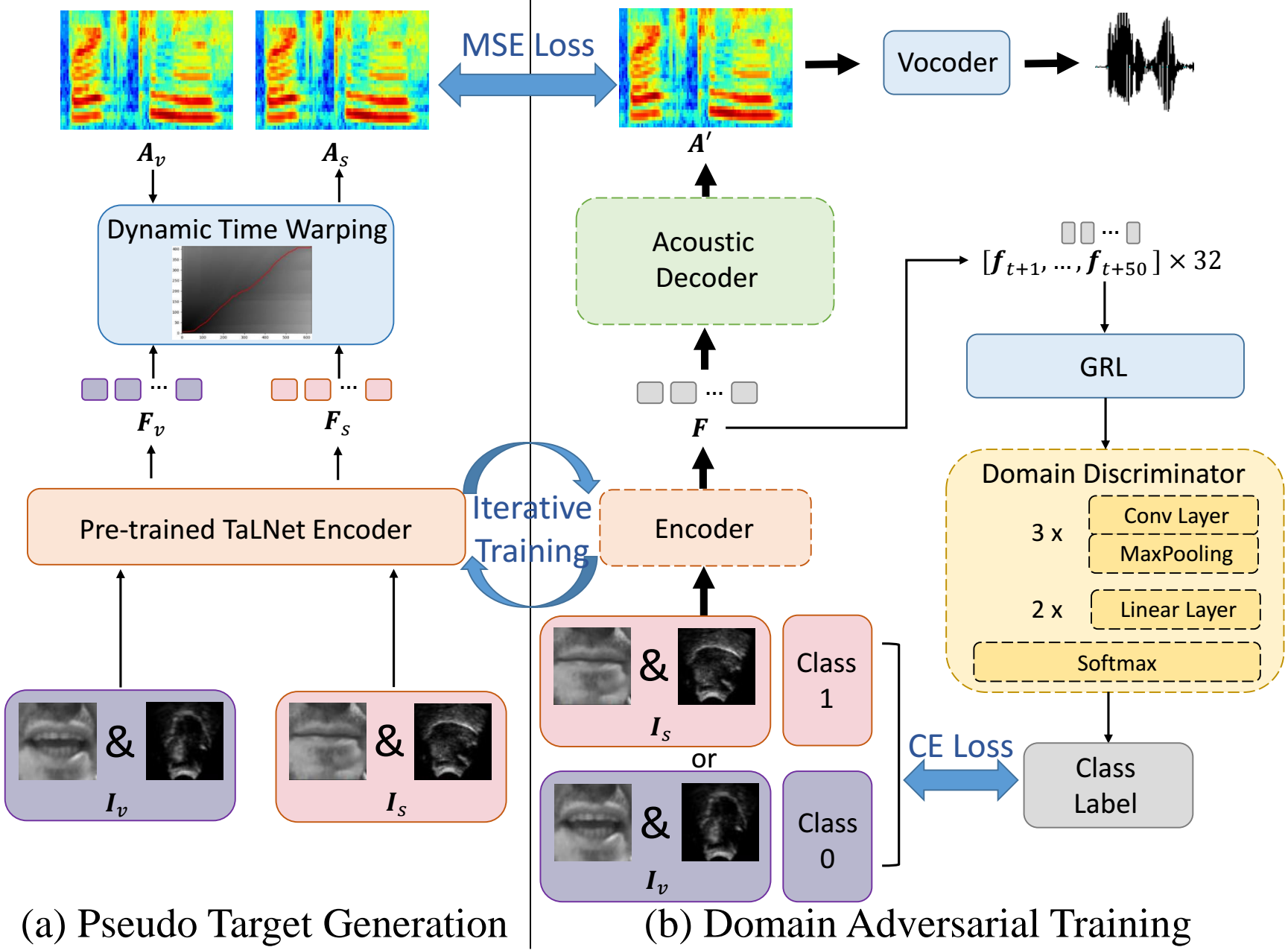
Rui-Chen Zheng, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
- This paper studies the task of speech reconstruction from ultrasound tongue images and optical lip videos recorded in a silent speaking mode, where people only activate their intra-oral and extra-oral articulators without producing sound. We propose to employ a method built on pseudo target generation and domain adversarial training with an iterative training strategy to improve the intelligibility and naturalness of the speech recovered from silent tongue and lip articulation. Experiments show that our proposed method significantly improves the intelligibility and naturalness of the reconstructed speech in silent speaking mode compared to the baseline TaLNet model.
🔑 Audio-Articulation Speech Enhancement
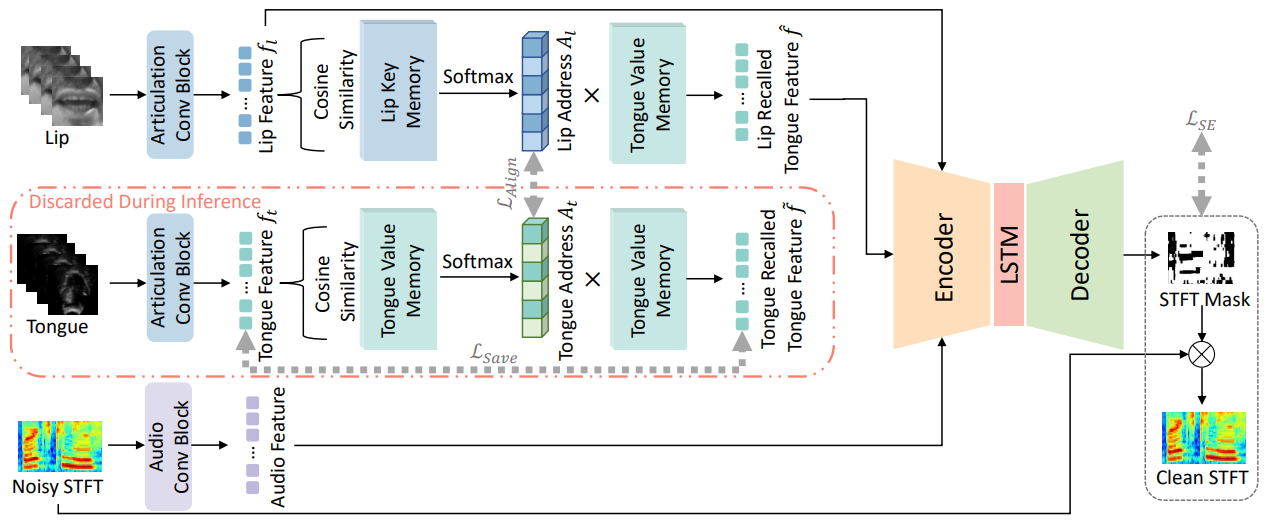
Incorporating Ultrasound Tongue Images for Audio-Visual Speech Enhancement
Rui-Chen Zheng, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
- This paper proposes the incorporation of ultrasound tongue images to improve the performance of lip-based audio-visual speech enhancement (AV-SE) systems. To address the challenge of acquiring ultrasound tongue images during inference, we first propose to employ knowledge distillation during training to investigate the feasibility of leveraging tongue-related information without directly inputting ultrasound tongue images. To better model the alignment between the lip and tongue modalities, we further propose the introduction of a lip-tongue key-value memory network into the AV-SE model. This network enables the retrieval of tongue features based on readily available lip features, thereby assisting the subsequent speech enhancement task. Experimental results demonstrate that both methods significantly improve the quality and intelligibility of the enhanced speech compared to traditional lip-based AV-SE baselines. Furthermore, phone error rate (PER) analysis of automatic speech recognition (ASR) reveals that while all phonemes benefit from introducing ultrasound tongue images, palatal and velar consonants benefit most.
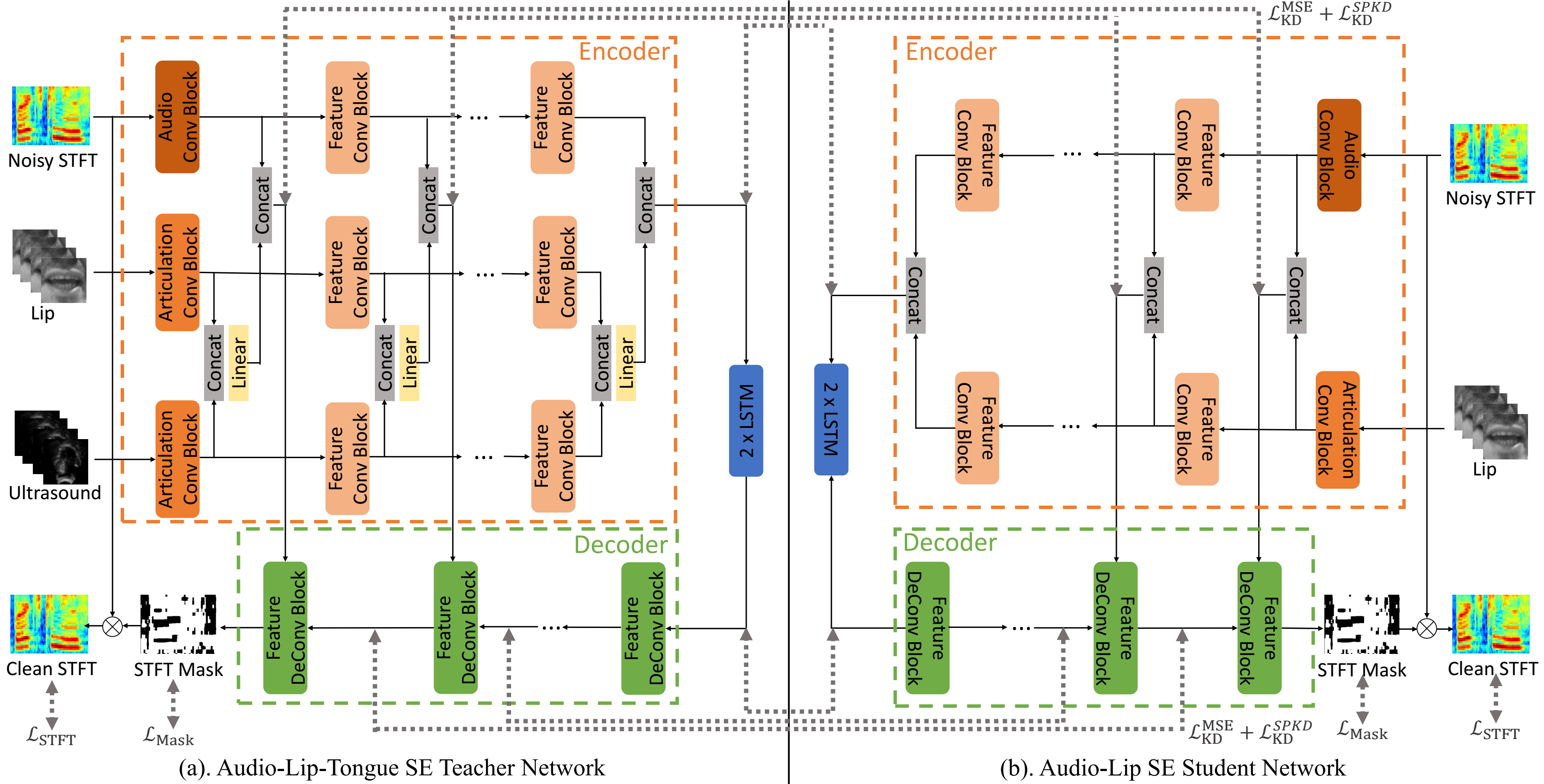
Rui-Chen Zheng, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
- Audio-visual speech enhancement (AV-SE) aims to enhance degraded speech along with extra visual information such as lip videos, and has been shown to be more effective than audio-only speech enhancement. This paper proposes further incorporating ultrasound tongue images to improve lip-based AV-SE systems’ performance. Knowledge distillation is employed at the training stage to address the challenge of acquiring ultrasound tongue images during inference, enabling an audio-lip speech enhancement student model to learn from a pre-trained audiolip-tongue speech enhancement teacher model. Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in the quality and intelligibility of the speech enhanced by the proposed method compared to the traditional audio-lip speech enhancement baselines. Further analysis using phone error rates (PER) of automatic speech recognition (ASR) shows that palatal and velar consonants benefit most from the introduction of ultrasound tongue images.
💬 End-to-end Spoken Dialogue System
- Accepted by ICASSP 2026 Understanding Textual Capability Degradation in Speech LLMs via Parameter Importance Analysis, Chao Wang*, Rui-Chen Zheng*(*Equal Contribution), Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling.
🎖 Honors and Awards
- 2025.10 National Graduate Scholarship.
- 2024.12 JAC-NIO Scholarship.
- 2021.06 Honor Rank for Top 5% Graduates of USTC.
- 2020.12 Huawei Scholarship.
- 2019.12 Top-Notch Program Funding.
- 2019.12 USTC Outstanding Student Scholarship, Gold Award.
🔍 Services
Invited Reviewers for Speech Communication, IEEE Signal Processing Letters and IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing.
📚 Teaching Assistant Experience
- 2022 Fall, Fundamentals of Speech Signal Processing, USTC (Prof. Zhen-Hua Ling)
- 2021 Fall, Fundamentals of Speech Signal Processing, USTC (Prof. Zhen-Hua Ling)
- 2020 Fall, Computer Programing Design A, USTC (Lecturer. Hu Si)
